|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
What is vision?
Vision is an anatomic, psychological, biophysical, and biochemical arrangement and mechanism within the retina that gives information to the brain and ultimately results in vision.
The eye is a biological camera we see from the brain, not from the retina.
There are three types of vision, and they are as follows.
- Monocular – vision with a single eye.
- Bi-Ocular – no coordination between two eyes, e.g. rabbit, buffalo, etc.
- Binocular – coordinated vision from two eyes, e.g. Humans, Eagles, Falcons, etc.
This article is mainly concentrated on binocular vision.
What is Binocular Vision?
Binocular vision can be defined as simultaneous vision with two eyes ( neither of which needs necessarily to be normal ) that occurs when an individual fixes his visual attention on an object.
In simple words, it is the coordinated use of two eyes to produce a single mental impression.
What does Normal binocular single vision require?
- Clear vision in both eyes.
- No manifest squint should be present.
- In both eyes, normal retinal correspondence is required.
- Coordination of two eyes for all directions of gazes.
- The ability of the brain to fuse both eye images in one.
There are three main grades in binocular vision.
- Simultaneous perception.
- Fusion.
- Stereopsis.
1) Simultaneous perception.
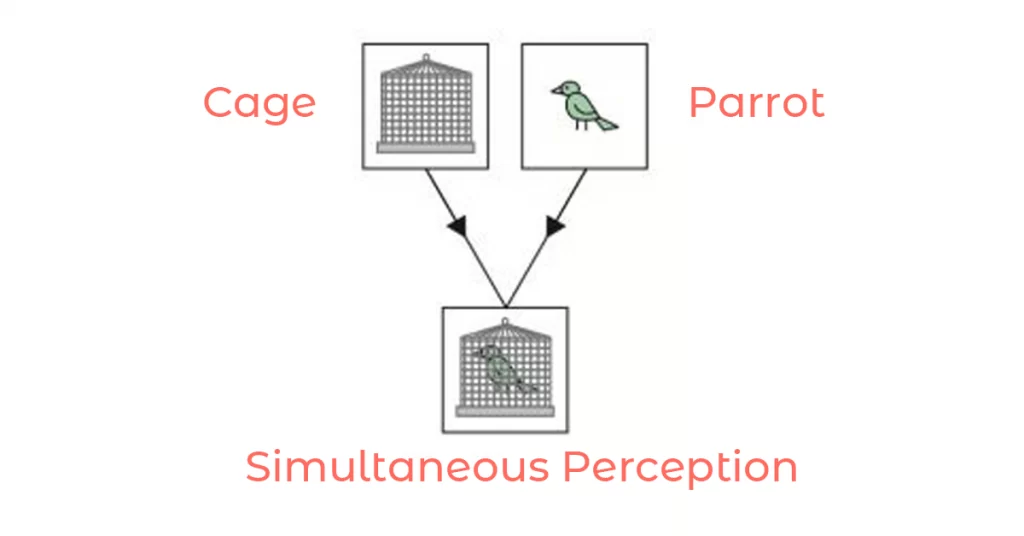
The term simultaneous perception does not imply on both eyes see the same object.
It consists of the power to see two dissimilar objects simultaneously.
It can be demonstrated by presenting separate stimuli to the two eyes, such as a cage picture to one eye and a picture of the parrot to the other eye.
If both cage and the bird see at the same time, then simultaneous perception is present.
2) Fusion
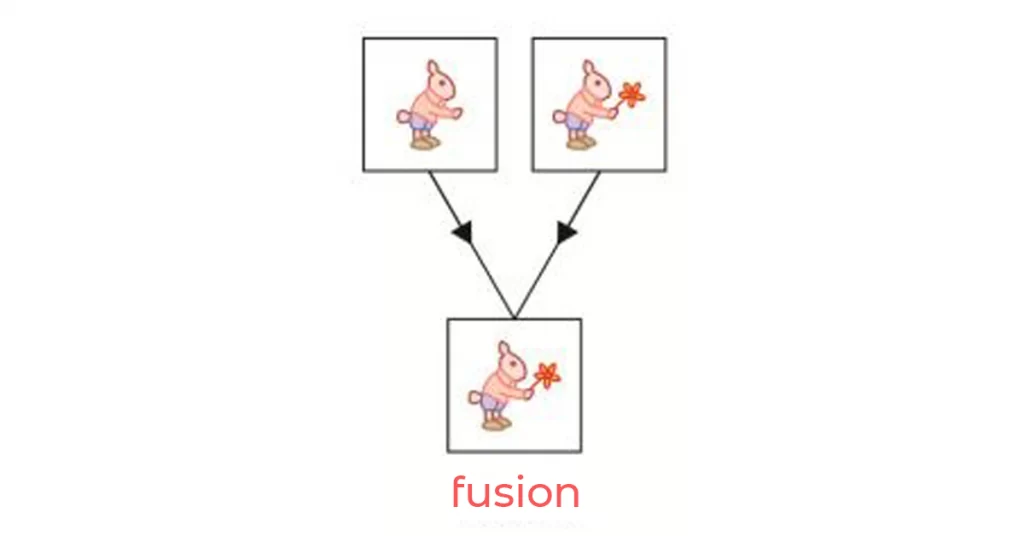
It implies the ability of two eyes to produce a composite picture from two similar pictures, each of which is incomplete with small detail.
For example, there are two rabbits, each lacking a tail or a bunch of flowers.
If fusion is present, one rabbit complete with a tail and holding a bunch of flowers will be seen.
3) Stereopsis
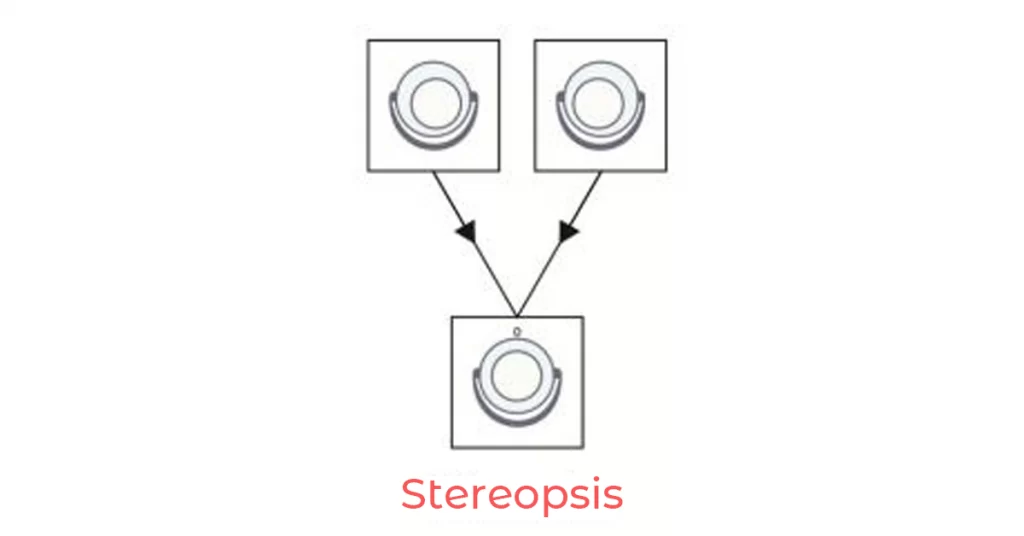
It can obtain an impression of depth by the supreme position of two pictures of the same objects, which have been taken from slightly different angles.
Stereopsis should not be synonymous with depth perception since depth perception is the distance of the object from each other or the observer.
Even a monocular observer is quite capable of judging distance and obtaining an impression of spatial order.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Binocular Vision
Advantages
- Large field of view and the person has good depth perception.
- Visual acuity is more.
- Contrast sensitivity is more.
- Color perception is more.
Disadvantages
- Diplopia ( Doubling of vision )
- ARC ( Abnormal retinal correspondence )
- Suppression ( subconscious adaptation by a person’s brain to eliminate the symptoms of disorders of binocular vision )
- Amblyopia. ( Partial loss of sight in one or both eyes )
What is binocular vision disorder?
Binocular vision disorder is a condition where the patient eyes are unable to align properly.
Loss of coordination between two eyes causes strabismus.
What is binocular dysfunction?
No coordination between the two eyes. This condition is called dysfunction of binocular vision.
It is making it difficult for the two eyes to work together.
It can lead to strabismus, dizziness, headache, light sensitivity, blur vision.
How to treat binocular vision dysfunction?
Binocular vision dysfunction is easily treated through eyeglasses, vision therapy, or surgery.
Therapy – pencil pushup test.
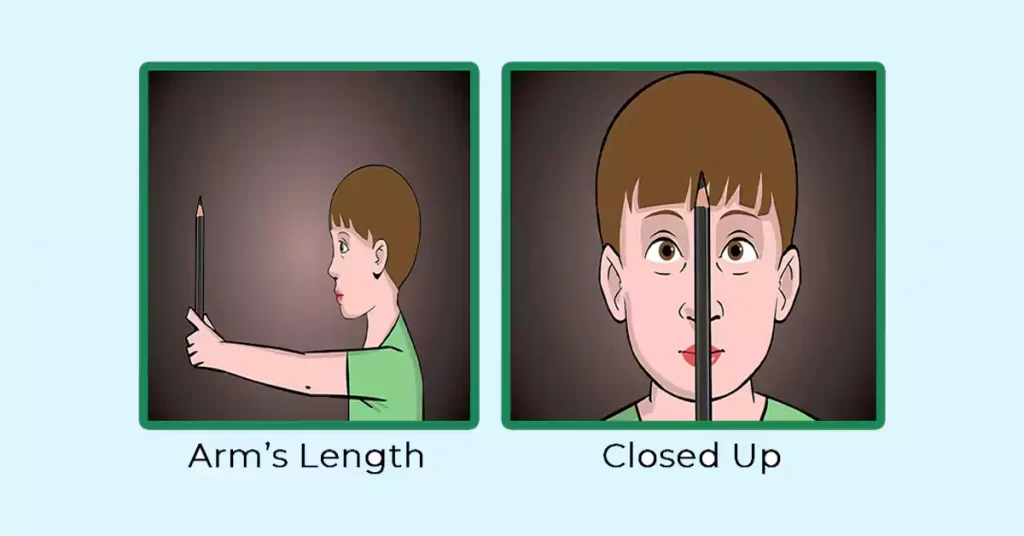
Pencil Pushup test: In the Pencil pushup test, the patient is told to focus on the tip of the pencil, then ask the patient to slowly bring it closer until the patient sees a doubling of the pencil and start the exercise again. This exercise is supposed to be done for 15min a day, 5 days a week.
How to test binocular Vision?
Stereopsis tests are available in various designs and produce a three-dimensional object in a variety of different ways.
Most tests use simple geometrical shapes as test objects presented against a random pattern background.
- Synaptophore
- Vectograph test
Synaptophore
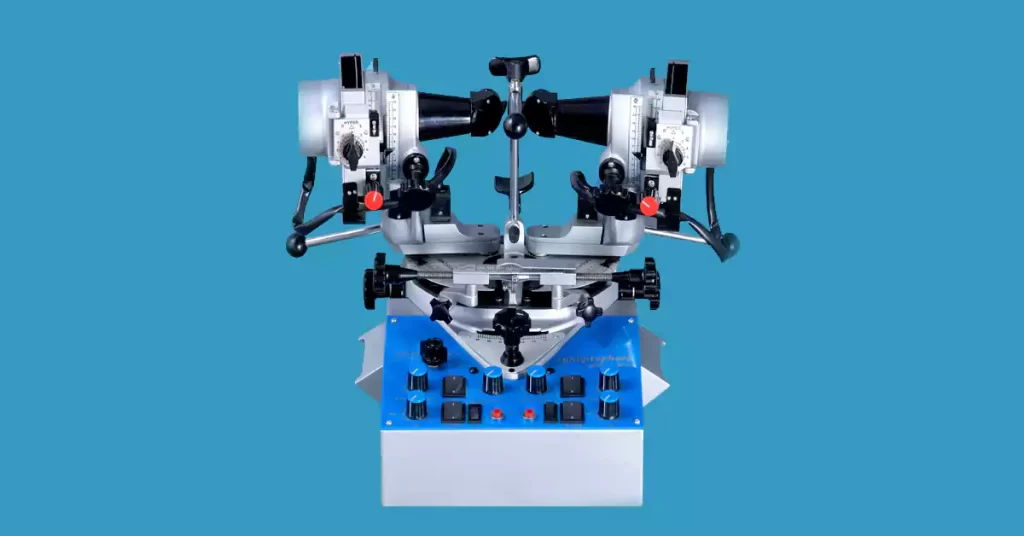
An instrument for diagnosing imbalances of eye muscle and treating them by the orthoptic method.
Vectograph Tests

A vecto graph consists of polaroid material on which the two targets are imprinted so that each target is polarized at 90 degrees to the other. The vecto graph dissociates the eyes optically. With the use of properly oriented spectacles, each target is seen separately with the two eyes.
Vecto graph is divided into two groups:
Group 1 – Titmus Stereogram
- The titmus fly test.
- Circle test.
- The Titmus animal test
Group 2 – Random Dot Stereogram
- Random dot E test (RDT).
- Random Dot TNO test.
- Lang test.
- Frisby test.








